参与者
- 表达式接口:这是我们的表达式的蓝图,定义了一种解释不同类型表达式的方法。
- 终端表达式:这些是返回值的主要表达式。
- 非终端表达式:这些表达式表示操作并使用终端表达式来完成其任务
参与者
工厂方法模式在 PHP 代码中被广泛使用。当您需要为代码提供高度灵活性时,它非常有用。
案例:手机加工
定义interface
interface PhoneProcessInterface {
public function process($phone_info);
}
定义各种手机加工的厂商
class IphoneProcess implements PhoneProcessInterface {
public function process($phone_info)
{
echo 'iphone process....';
}
}
class HuaweiProcess implements PhoneProcessInterface {
public function process($phone_info)
{
echo 'Huawei process....';
}
}
class SamsungProcess implements PhoneProcessInterface {
public function process($phone_info)
{
echo "SamSung process...";
}
}定义工厂会帮助实例化. 外部直接使用
class PhoneFactory {
public function samsung($phone_info) {
return (new SamsungProcess())->process($phone_info);
}
public function huawei($phone_info) {
return (new HuaweiProcess())->process($phone_info);
}
public function iphone($phone_info) {
return (new IphoneProcess())->process($phone_info);
}
}测试
$phone_info = [
'name' => 'iphone',
'version' => '15'
];
$phone_factory = new PhoneFactory();
if ($phone_info['name'] == 'iphone') {
$phone_factory->iphone($phone_info);
}
输出Iphone process
单例很简单就是一个类一个类只初始化一次
定义一个单例类
class Single {
protected static $instance = NULL;
public static function getInstance():static {
if (self::$instance == NULL) {
self::$instance = new static;
}
return self::$instance;
}
}
继承和使用
class DB extends Single {
}
class Logger extends Single {
}
$db = DB::getInstance();
$logger = Logger::getInstance();
如果我们需要的不仅仅是一个记录器实例,因为有些消息必须写入文件中,有些消息需要通过电子邮件发送
定义多例
class Multiple {
protected static array $instance = [];
public static function getInstance($key) {
if (!isset(self::$instance[$key])) {
self::$instance[$key] = new static;
}
return self::$instance[$key];
}
}
// 定义写入日志的接口
interface LoggerHanderInterface {
public function save($level, $message, $context);
}
定义3种写入日志的方式
class DbLogger implements LoggerHanderInterface {
public function save($level, $message, $context) {
print ("Save to db $level: $message");
}
}
class FileLogger implements LoggerHanderInterface {
public function save($level, $message, $context) {
print ("Save File$level: $message");
}
}
class MailLogger implements LoggerHanderInterface {
public function save($level, $message, $context) {
print ("Send mail $level: $message");
}
}
最后定义logger. 这里使用了psr\Log这个包.
class Logger extends Multiple implements \Psr\Log\LoggerInterface {
use \Psr\Log\LoggerTrait;
private LoggerHanderInterface $handle;
public function setHandle(LoggerHanderInterface $hander) {
$this->handle = $hander;
}
public function log($level, $message, array $context = array())
{
$this->handle->save($level, $message, $context);
}
}
测试
$db_logger = Logger::getInstance('db');
$db_logger->setHandle(new DbLogger());
$file_logger = Logger::getInstance('file');
$file_logger->setHandle(new FileLogger());
$mail_logger = Logger::getInstance('mail');
$mail_logger->setHandle(new MailLogger());
// 打印hander 是 DbLogger
$logger1 = Logger::getInstance('db');
var_dump($logger1);
// 打印hander 是 DbLogger
$logger2 = Logger::getInstance('db');
var_dump($logger2);
// 打印hander 是 MailLogger
$logger3 = Logger::getInstance('mail');
var_dump($logger3);
当你需要操作别人遗留下来的项目,或者说第三方的代码的时候。尤其是通常情况下,这些代码你不容易去重构它们,也没有提供测试(tests)。这个时候,你就可以创建一个facade(“外观”),去将原来的代码“包裹”起来,以此来简化或优化其使用场景。
当一个对象或者数据有多种展示方式的时候用装饰者模式. 比如数组可以以json, xml的展示方式. 再比如用户数据A页面会有一种展示方式. B页面会有一种展示方式
现在来用装饰者模式展示array. 先定义一个对象用来接受数组和输出输出.
class OutputData {
private DecoratorInterface $decorator;
public function __construct(private array $data) {}
public function setDecorator(DecoratorInterface $decorator) {
$this->decorator = $decorator;
}
public function output() {
return $this->decorator->renderData($this->data);
}
}
定义装饰者, 分别定义JSON和XML
interface DecoratorInterface {
public function renderData($data);
}
class XMLRender implements DecoratorInterface {
function toXml(SimpleXMLElement $object, array $data) {
foreach ($data as $key => $value) {
// if the key is an integer, it needs text with it to actually work.
$valid_key = is_numeric($key) ? "key_$key" : $key;
$new_object = $object->addChild(
$valid_key,
is_array($value) ? null : htmlspecialchars($value)
);
if (is_array($value)) {
$this->toXml($new_object, $value);
}
}
}
public function renderData($data) {
$xml = new SimpleXMLElement('<root/>');
$this->toXml($xml, $data);
return $xml->saveXML();
}
}
class JsonRender implements DecoratorInterface {
public function renderData($data) {
return json_encode($data);
}
}
最后根据所需输出指定类型
$data = new OutputArray([
'books' => [
'Abook',
'Bbook',
'Cbook'
],
'cart' => [
'Acart',
'Bcart',
'Ccart'
]
]);
$data->setDecorator(new XMLRender());
$data->setDecorator(new JsonRender());
print_r($data->output());
定义菜品接口
interface FoodItem {
// 定义附加的成本.
public function cost();
}
// 定义一个手抓饼. 成本为10块钱.
class HandCake implements FoodItem {
private array $items = [];
public function cost() {
return 10;
}
public function addItem(FoodItem $item) {
$this->items[] = $item;
}
public function Calculation() {
$total = $this->cost();
foreach ($this->items as $item) {
$total += $item->cost();
}
return $total;
}
}
定义小菜可选增加
// 定义鸡蛋小菜的成品为4块
class Egg implements FoodItem {
public function cost () {
return 4;
}
}
// 定义一个火腿价格为6块
class Ham implements FoodItem {
public function cost () {
return 6;
}
}
$handcake = new HandCake();
$handcake->addItem(new Egg());
$handcake->addItem(new Egg());
$handcake->addItem(new Egg());
$handcake->addItem(new Ham());
$handcake->addItem(new Ham());
print $handcake->Calculation();定义一个商品类
class Product {
public string $title;
public float $price;
}定义活动接口
interface ProductActivities {
public function getReduce(Product $product);
}定义活动
// 双十一减5块.
class Two11 implements ProductActivities {
public function getReduce($product) {
return 5;
}
}
// 满500减50.
class Filled500 implements ProductActivities {
public function getReduce(Product $product) {
if ($product->price > 500) {
return 50;
}
}
}
定义产品建造者来获取产品
class ProductBuilder {
private Product $product;
private array $activities;
public function __construct($title, $price) {
$product = new Product();
$product->title = $title;
$product->price = $price;
$this->product = $product;
}
/**
* 获取商品.
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function getProduct() {
// 根据活动重新计算减少的价格.
$price = $this->product->price;
foreach ($this->activities as $activity) {
$price -= (int)$activity->getReduce($this->product);
}
$this->product->price = $price;
return $this->product;
}
/**
* 添加活动.
*
* @param $activity
*/
public function addActivity($activity) {
$this->activities[] = $activity;
}
}最后测试
$product = new ProductBuilder('Iphone16', '9000');
$product->addActivity(new Two11());
$product->addActivity(new Filled500());
print_r($product->getProduct());
//建造者模式,目的是消除其它对象复杂的创建过程
/* 描述一个用户的类,包含用户姓名,年龄,金钱 */
class UserInfo {
protected $userName = '';
protected $userAge = '';
protected $userMoney = '';
public function setUserName($userName) {
$this->userName = $userName;
}
public function setUserAge($userAge) {
$this->userAge = $userAge;
}
public function setUserMoney($userMoney) {
$this->userMoney = $userMoney;
}
public function getPeople() {
echo "这个人的姓名是:" . $this->setUserName . ',年龄是:' . $this->userAge . ', 金钱:' . $this->userMoney;
}
}
/* 实例化,并且创建这个用户的时候,是很痛苦的,需要设置用户名,年龄和金钱*/
$peopleInfo = array(
'userName' = 'initphp',
'userAge' = 28,
'userMoney' = '100元'
);
$UserInfo = new UserInfo;
//下面需要一步步的设置用户信息,才能得到用户详细信息,过程纠结而痛苦
$UserInfo->setUserName($peopleInfo['userName']);
$UserInfo->setUserAge($peopleInfo['userAge']);
$UserInfo->setUserMoney($peopleInfo['userMoney']);
$UserInfo->getPeople();
//UserInfoBuilder 用户信息建造者类,将UserInfo的创建过程封装掉,开发者使用起来心情舒畅
<?php
//建造者模式,目的是消除其它对象复杂的创建过程
include("UserInfo.php");
class UserInfoBuilder {
protected $obj;
public function __construct() {
$this->obj = new UserInfo;
}
public function buildPeople($peopleInfo) {
$this->obj->setUserName($peopleInfo['userName']);
$this->obj->setUserAge($peopleInfo['userAge']);
$this->obj->setUserMoney($peopleInfo['userMoney']);
}
public function getPeople() {
$this->obj->getPeople();
}
}
/* 创建过程被封装了,用户使用简单了 */
$peopleInfo = array(
'userName' = 'initphp',
'userAge' = 28,
'userMoney' = '100元'
);
$UserInfoBuilder = new UserInfoBuilder;
$UserInfoBuilder->buildPeople($peopleInfo); //直接一个build
$UserInfoBuilder->getPeople();文章来源于: https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1723155
适配器模式就是保留现有类所提供的功能和服务 在不改变原有系统的基础上提供新的接口服务. 比如苹果笔记本并不支持直接插入网线. 而想要插入网线就需要买一个适配器. 这个适配器可以只支持插入网线也可以是功能强大的支持各种插口
使用场景如下:
需求.
先定义一个模块来完成我们的需求. 模块名为.
use Drupal\user\UserInterface;
/**
* Implements hook_user_login().
*
* @param UserInterface $account
* @throws \Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityMalformedException
*/
function observer_user_login(UserInterface $account) {
// ############# 用户登陆成功根据用户的专业给用户推送产品. ########## //
switch ($account->get('field_profession')->value) {
case 'A':
//一大堆逻辑
break;
case 'B':
// 一大堆逻辑
break;
case 'C':
// 一大堆逻辑
break;
default:
// 一大堆逻辑
break;
}
// ############# 用户登陆成功给用户发送一封邮件. ########## //
// 发送邮件逻辑
// ############# 用户登陆成功判断后一次登陆时间如果超过1个月告诉通知营销部门. ########## //
if (time() - $account->get('access')->value > 3000) {
// 通知营销部门逻辑
}
// ############# 用户登陆成功如果角色是超级管理员自动跳转到 /admin/contents 页面. ########## //
if ($account->hasRole('administrator')) {
// 跳转逻辑
}
// ############# 用户登陆成功如果角色是网站管理员自动跳转到 /manage页面. ########## //
if ($account->hasRole('webmaster')) {
// 跳转逻辑
}
}这里的代码越后面会越乱,如果到时再增加一个需求登陆成功要做某事。可能又是一大堆逻辑.
现在改用普通的PHP观察者模式分离代码
定义: src/Observer.php
<?php
namespace Drupal\observer;
use Drupal\user\UserInterface;
/**
* 创建主题用来注册所有的观察者.
*
* Class Observer
*/
class Observer implements \SplSubject {
private array $observers = [];
private UserInterface $account;
public function setAccount(UserInterface $account) {
$this->account = $account;
}
public function getAccount() {
return $this->account;
}
/**
* 注册观察者.
*
* @param \SplObserver $observer
*/
public function attach(\SplObserver $observer):void {
$this->observers[] = $observer;
}
/**
* 移掉观察者.
*
* @param \SplObserver $observer
*/
public function detach(\SplObserver $observer):void {
if ($key = array_search($observer,$this->observers, true)){
unset($this->observers[$key]);
}
}
/**
* 通知观察者.
*/
public function notify():void {
foreach ($this->observers as $value) {
$value->update($this);
}
}
}
分别定义功能代码:
src/Observers/Notice.php
src/Observers/NoticeMarkting.php
src/Observers/PushProduct.php
src/Observers/RedAdmin.php
src/Observers/RedWebmaster.php
代码都类似如下。只是类名不一样.
<?php
namespace Drupal\observer\Observers;
use Drupal\observer\Observer;
use SplSubject;
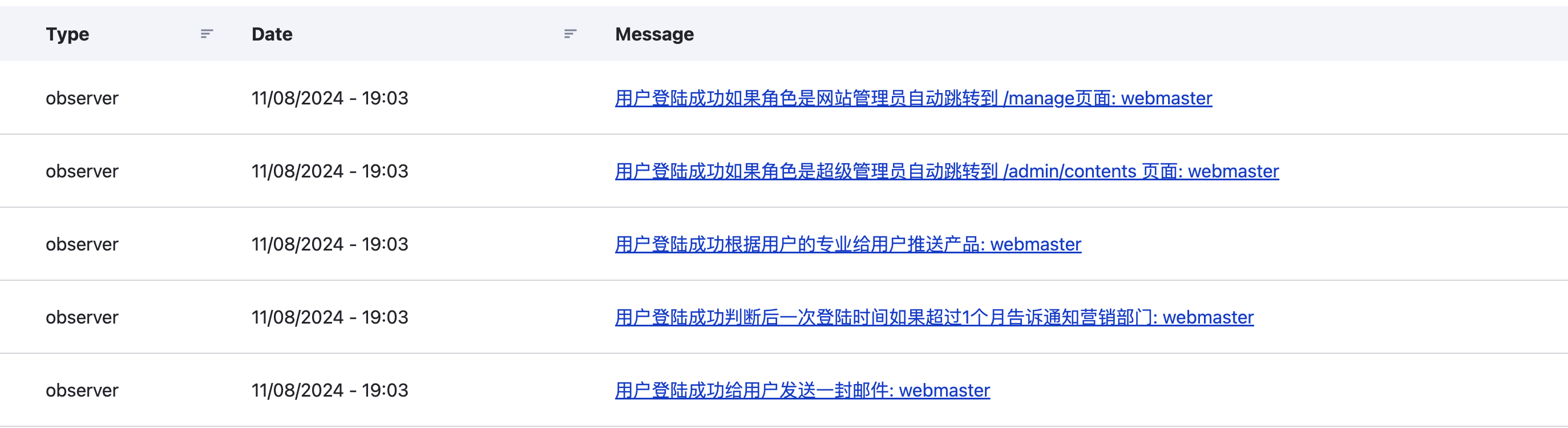
class Notice implements \SplObserver {
public function update(Observer|SplSubject $subject):void {
$account = $subject->getAccount();
\Drupal::logger('observer')->notice('用户登陆成功给用户发送一封邮件: ' . $account->label());
}
}
然后修改hook
<?php
use Drupal\observer\Observers\Notice;
use Drupal\observer\Observers\NoticeMarkting;
use Drupal\observer\Observers\PushProduct;
use Drupal\observer\Observers\RedAdmin;
use Drupal\observer\Observers\RedWebmaster;
use Drupal\user\UserInterface;
use Drupal\observer\Observer;
/**
* Implements hook_user_login().
*
* @param UserInterface $account
*/
function observer_user_login(UserInterface $account) {
$observer = new Observer();
$observer->setAccount($account);
$observer->attach(new Notice());
$observer->attach(new NoticeMarkting());
$observer->attach(new PushProduct());
$observer->attach(new RedAdmin());
$observer->attach(new RedWebmaster());
$observer->notify();
}
Drupal的event和hook就很类似观察者模式. 现在可以使用event来实现这段代码
这里定义一个新的模块: obevent
先自定义一个用户登陆的事件: src/Event/UserLoginEvent.php
<?php
namespace Drupal\obevent\Event;
use Drupal\Component\EventDispatcher\Event;
use Drupal\user\UserInterface;
class UserLoginEvent extends Event {
const EVENT_NAME = 'custom_event_user_login';
/**
* @var \Drupal\user\UserInterface
*/
public UserInterface $account;
public function getAccount() {
return $this->account;
}
public function setAccount($account) {
$this->account = $account;
}
public function __construct(UserInterface $account) {
$this->setAccount($account);
}
}
定义功能实现的服务: obevent.services.yml
services:
obevent.user_login_notice_event_subscriber:
class: Drupal\obevent\EventSubscriber\LoginNoticeSubscriber
tags:
- { name: event_subscriber }
obevent.user_login_notice_markting_event_subscriber:
class: Drupal\obevent\EventSubscriber\LoginNoticeMarktingSubscriber
tags:
- { name: event_subscriber }
obevent.user_login_push_product_event_subscriber:
class: Drupal\obevent\EventSubscriber\LoginPushProductSubscriber
tags:
- { name: event_subscriber }
obevent.user_login_red_admin_subscriber:
class: Drupal\obevent\EventSubscriber\LoginRedAdminSubscriber
tags:
- { name: event_subscriber }
obevent.user_login_red_webmater_subscriber:
class: Drupal\obevent\EventSubscriber\LoginRedWebmasterSubscriber
tags:
- { name: event_subscriber }
定义功能实现代码:
src/EventSubscriber/LoginNoticeMarktingSubscriber.php
src/EventSubscriber/LoginNoticeSubscriber.php
src/EventSubscriber/LoginPushProductSubscriber.php
src/EventSubscriber/LoginRedAdminSubscriber.php
src/EventSubscriber/LoginRedWebmasterSubscriber.php
功能类似下面这样. 只是类名不一样
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace Drupal\obevent\EventSubscriber;
use Drupal\obevent\Event\UserLoginEvent;
use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventSubscriberInterface;
final class LoginNoticeSubscriber implements EventSubscriberInterface {
/**
* Kernel request event handler.
*/
public function onUserLogin(UserLoginEvent $event): void {
$account = $event->getAccount();
\Drupal::logger('observer')->notice('用户登陆成功给用户发送一封邮件: ' . $account->label());
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public static function getSubscribedEvents(): array {
return [
UserLoginEvent::EVENT_NAME => ['onUserLogin'],
];
}
}
修改obevent.module文件.
<?php
use Drupal\obevent\Event\UserLoginEvent;
use Drupal\user\UserInterface;
/**
* Implements hook_user_login().
*
* @param UserInterface $account
*/
function obevent_user_login(UserInterface $account) {
$event = new UserLoginEvent($account);
\Drupal::service('event_dispatcher')->dispatch($event, UserLoginEvent::EVENT_NAME);
}